Food Chain Dynamics Biology Diagrams As a man-made structure, artificial reef is regarded as an effective tool for protecting and supporting the marine environment and restoring habitats (Mclean et al., 2015, Chen et al., 2019, Tang et al., 2021), which not only create suitable habitats for the growth, breeding, forage and defense of marine organisms (Sherman et al., 2002), but also mitigate habitat loss and protect
Food chain is a linear sequence that depicts the flow of energy and nutrients in an ecosystem through various organisms. It begins with producers (plants or autotrophs) that capture solar energy and create food through photosynthesis. This energy is transferred to primary consumers (herbivores), then to secondary and tertiary consumers (carnivores and omnivores), and finally…

Definition, Examples, Types Biology Diagrams
Habitat destruction, characterized by habitat loss and fragmentation, is a key driver of species extinction in spatial extended communities. Recently, there has been some progress in the theory of spatial food webs, however to date practically little is known about how habitat configurational fragmentation influences multi-trophic food web dynamics. Aquatic plants are indispensable to pond ecosystems, offering shelter, oxygen, and food to various species. Types of Aquatic Plants. Algae: Although more common in oceans, algae form the base of the pond food chain. Submerged Plants: Fully underwater, these include bladderwort and pondweed.
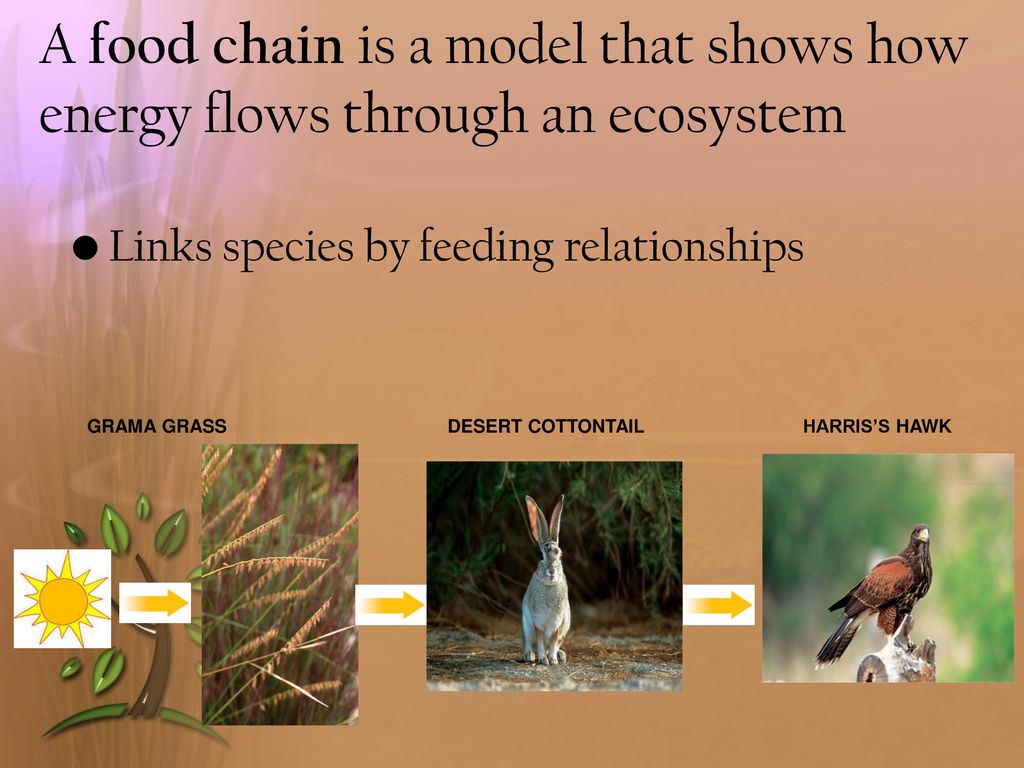
By studying food chains, ecologists better understand ecosystem dynamics, including the flow of energy, population control, and the impact of human activities on natural habitats. Key Points Food chains are linear models that illustrate energy transfer from producers to top consumers. 2012 The dynamics of food chains under climate change and nutrient enrichment Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B Lassus R, Morla J, Daufresne M and Sentis A (2024) Direct effect of artificial warming on communities is stronger than its indirect effect through Vieira R and Sturrock A (2024) Fish habitat ecology in a changing climate, Journal of Fish

The dynamics of food chains under climate change and nutrient ... Biology Diagrams
Habitat complexity is a key-driver of biodiversity in a range of different ecosystems such as upland streams, temperate lakes, and deciduous forests (Dean and Connell, 1987; Downes et al., 1998; Kostylev et al., 2005; Lawton, 1983; MacArthur and MacArthur, 1961).For example, branching trees support fish biodiversity in temperate lakes (Newbrey et al., 2005), and the height profile of foliage
