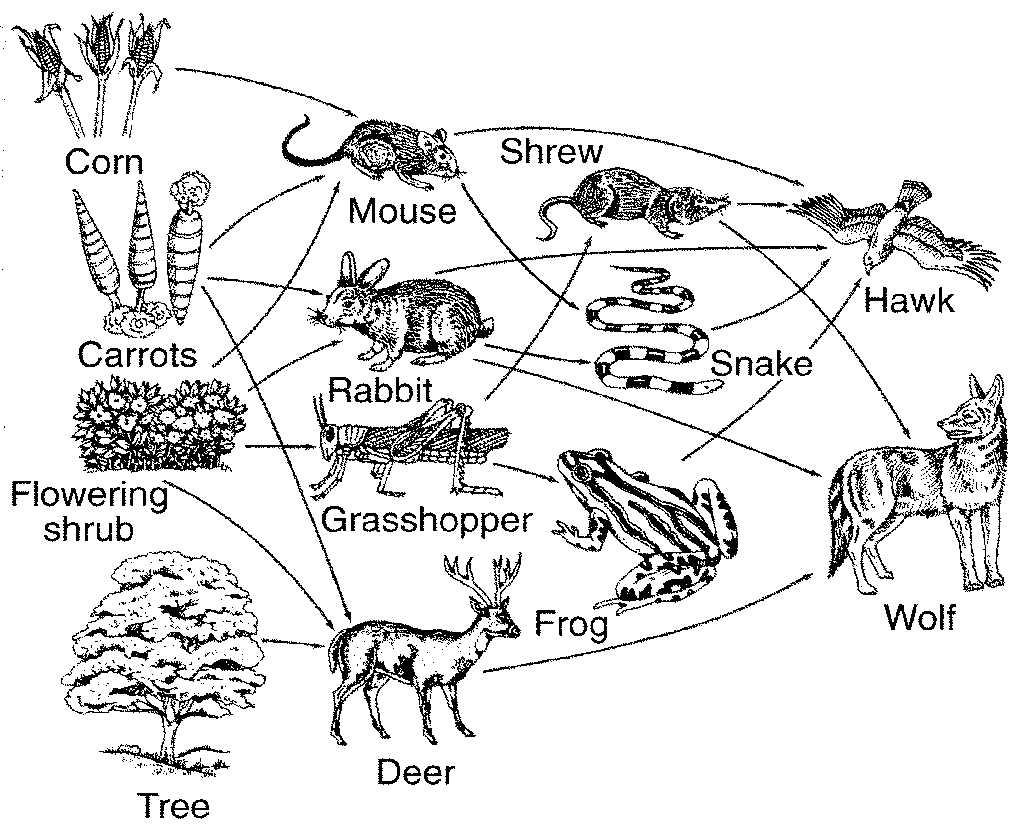
Wetlands Activity Sheets Biology Diagrams In the Lake Ontario food chain, shown in figure 6.1.1.4.g 6.1.1.4. g, the Chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. Some communities have additional trophic levels (quaternary consumers, fifth order consumers, etc.). Finally, detritivores and decomposers break down dead and decaying organisms from any trophic level.
Explore the intricacies of wetland food webs, uncovering the dynamics that sustain biodiversity and ecosystem health in vital wetlands.

PDF Exploring the Food Web Biology Diagrams
Students diagram a wetland food chain identifying producers, consumers, and decomposers, then they use their food chain diagrams to illustrate the fl ow of energy through the carbon cycle. The lesson ends with a short student research activity to assist them in further understanding a wetland ecosystem. Food chain: a series of living things that are dependent on the next as a source of food List some wetland plants and animals in the box below: Now list the words from above in the spaces below to make your own food chain: Wetland Food Chains, continued on page 4 Wetland Food Chains, continued from page 3 Vocabulary to know: n The "Wetlands" unit includes three activities that are designed to promote an understanding of the transfer of nutrients and energy through food chains and food webs. Students recognize the interdependence of all living things by this comparison. The activities illustrate the basic ecological components of a wetland ecosystem, their relationship via food chains, and finally the flow and loss

Procedure Read the background material aloud in class. It may be helpful to draw an example of a food chain or food web on the board, and to make a diagram with producers on the bottom, with the primary consumers above them, the secondary consumers above the primary consumers, and so on. Make food web cards (from the list below) on large index

PDF LeSSON 1 The Wetland ecosystem Biology Diagrams
Food Chains and Food Webs by Karen Marks Oh what a tangled web we weave, when first we start to feed A simple food chain begins with the sun. Plants absorb sunlight and use this energy in the process of photosynthesis to create simple organic compounds otherwise known as carbohydrates (sugar). This form of "food" provides energy to the plant itself and to animals that eat the plant
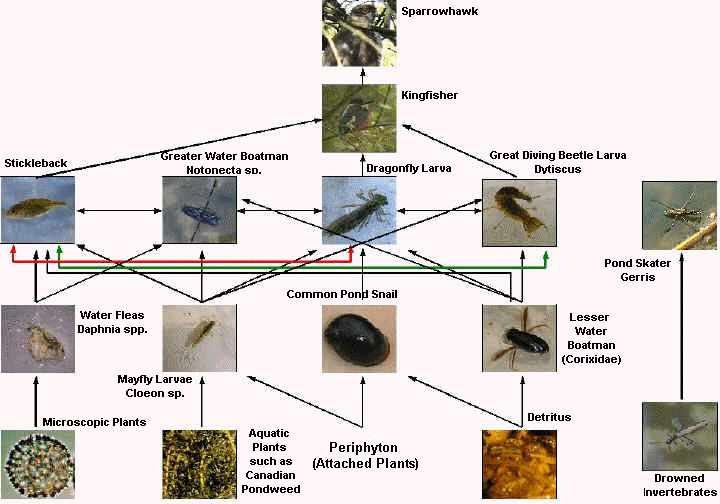
A wetland food chain is a diagram that shows the flow of energy through different species in a linear direction. Food chains are divided into layers called trophic levels.